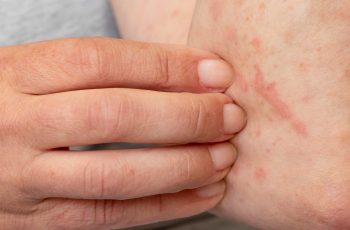
Eczema affects over 31.6 million people in the U.S., with atopic dermatitis being the most common type. It can manifest as red, chapped skin, and in darker skin tones, it may appear gray, purple, or brown. Various demographics show differing prevalence rates, with around 10% of African Americans, 13% of Asian Americans, 11% of whites, and 13% of Native Americans affected. While there is no complete cure for eczema, lifestyle changes, creams, and natural remedies can help manage symptoms, especially during winter flare-ups.
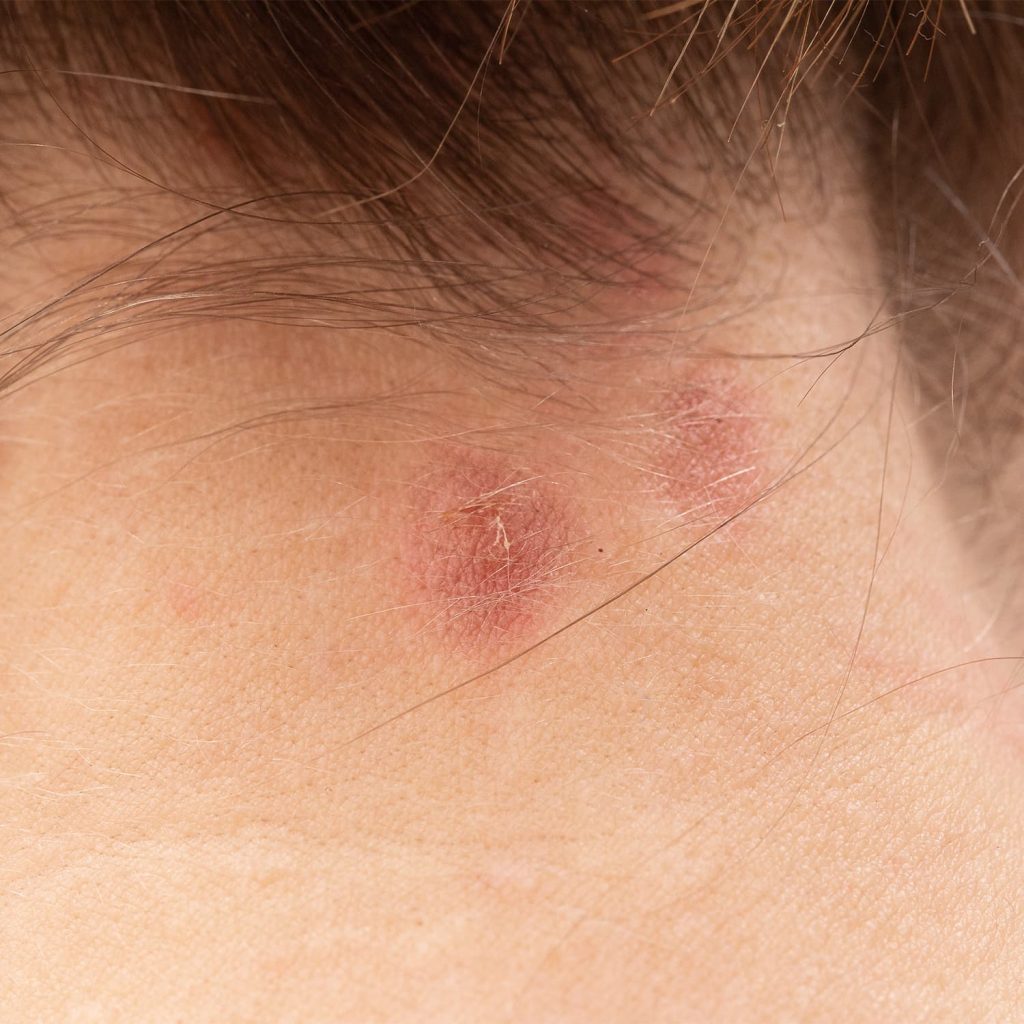
What is Eczema?
Eczema encompasses various conditions that cause skin irritation and inflammation. Atopic dermatitis is the most prevalent form, affecting about 10-20% of infants and 3% of adults. Symptoms include itching, redness, and dry, cracked skin. Eczema is not contagious.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary by age. In infants, rashes often ooze and crust, typically affecting the face and scalp. In children and teens, rashes appear in the elbow bends and behind the knees. Adults may experience dry, scaly patches on the face, hands, and other areas.
Types of Eczema
- Atopic Eczema: Most common, linked to allergies.
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by skin contact with irritants or allergens.
- Irritant Dermatitis: Commonly caused by chemicals.
- Allergic Dermatitis: Reaction to allergens like nickel or latex.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Causes blisters on hands and feet.
- Neurodermatitis: Characterized by itchy patches.
- Nummular Eczema: Coin-shaped patches often after skin injury.
Natural Remedies
- Colloidal Oatmeal: Soothes inflamed skin.
- Evening Primrose Oil: May reduce inflammation.
- Coconut Oil: Moisturizes and has antibacterial properties.
- Sunflower Oil: Hydrates and protects the skin.
- Witch Hazel: Calms inflammation.
- Calendula Cream: May relieve symptoms.
- Acupuncture/Acupressure: Potentially reduces itching.
- Relaxation Techniques: Help manage stress, a common trigger.
- Honey: Antibacterial and promotes healing.
Final Thoughts
Avoid irritants like perfumed products and consider dietary changes to manage eczema. While home remedies can help, severe cases may require medical treatment. Consult your doctor for a tailored treatment plan.